 GE imagination at work
GE imagination at work
How do I manually install the PITC certificate to my server or application?
| Process | Behavior | Quick Link to process |
|---|---|---|
| Installing to the local computer for Windows Server | Certificate is added to the local computer’s cert store. All user accounts will have installed certificate in their local user certificate store. Additional users will not need to repeat the process. | Installing Certificate for the local computer |
| Installing to the local user account for Windows Server (NOTE: not required if certificate is installed to the local computer) | Certificate is added to the local certificate store of the account that is logged in and completing the process. Note, manual per user installation is required if Firefox is in use on the server due to the use of a proprietary cert store. | Installing Certificate for your local user account |
| Installing for Amazon, Enterprise and Oracle Release 7 or greater | Certificate is added to the trusted Anchors using ca-certificates package | Installing Certificate for Linux through ca-certificates |
| Installing for versions 5 and 6 of Enterprise and Oracle Linux | Certificate is installed by adding the certificate to ca-bundle.crt | Installing Certificate for Linux by adding to ca-bundle.crt file |
| Installing for Middleware IBM Web Sphere | Sample middleware installation | Installing Certificate for Middleware, WebSphere example |
| Installing for *nix Java cert stores | Certificate is added to special Java locations | Installing GE Certificate in a *nix Java Store |
Where can I download the certificate?
Before you start with either process, you will need to have the following certificate:
DER encoded certificate can be downloaded from here: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
PEM encoded certificate can be downloaded from here: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt.
See later paragraphs to determine which encoding you need.
How do I test to see if I have the certificate needed to access the Internet?
In addition to manually reviewing the certificate stores on the server, there are two tools that can be used to detect if the certs are present on you system. First when the user attempts to browse the Internet on a graphical server console, the PITC cert validation page will pop up if needed certificate is not installed. Please see the next section for a depiction of this popup.
Additionally, a user may browse to http://internet.ge.com/certcheck and quickly check to see if their system is updated and has the proper software. Depending on state, the user will receive a visual representation of if their computer and browser complies.


Note: just because your server’s browser says "Your’re ready!" that doesn’t mean that middleware on your server is ready. Please always perform a full test.
For *nix based operating systems, you can test against the following URLs with either wget or cURL.
The syntax for both commands is as follows:
wget --no-cache https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -e https_proxy=PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
curl https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -x PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
Deployment Note for older versions of Microsoft Windows Operating Systems and Microsoft Internet Explorer
Please note that in some cases certificate installation validation may fail with older versions of Server and Internet Explorer, e.g. Server 2003 using Internet Explorer 7. Failures in this case is often due to a lack of support for higher level TLS standards or due to enhanced security controls. If this occurs in your installation, please try to use a different browser, e.g. Google Chrome or a modern version of Internet Explorer, to test.
Where is the certificate installed?
The following table describes where certificate is installed from the context of the operating system. NOTE: supporting applications may also need the certificate installed into an "App" specific store. This may be true for many java based applications. Please consult vendor documentation for your applications to see if this applies to you.
| Certificate | Windows Server 2008, 2012 | Amazon, Enterprise and Oracle Release 7 or greater | Enterprise and Oracle Linux versions 5 and 6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE External Root CA 2.1 | Trusted Root Certificate Authorities | /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ | /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt |
Where can I find more information about installing the certificate for other operating systems or applications?
As this SOP is sample and does not cover all potential operating systems and applications in production, for non-listed operating systems or applications consult vendor documentation related to how to import self-signed root certificate into the operating system or application’s trusted root certificate authorities file or logical store. If you are searching the web for this information, please search for how to import self-signed root certificate for your application or operating system.
Next steps?
None. The whole process of installing the additional certificate is viewed to be transparent.
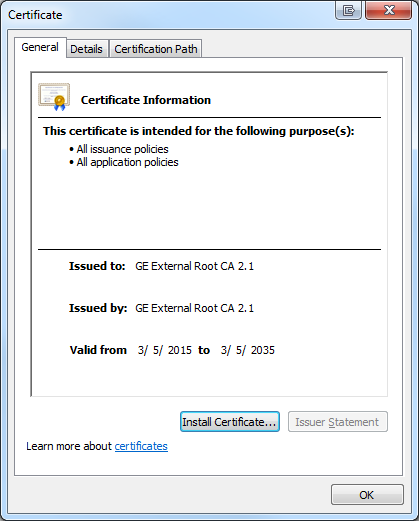
 Installing Certificate for the local computer with Windows Server
Installing Certificate for the local computer with Windows Server
DER encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
Procedurally, certificate will be installed from the Certificate snap-in to the Microsoft Management Console. To add this MMC snap in, perform the following procedure. Note this process has been validated for both Windows 2008 and 2012.
In addition to the below GUI approach, the following command line can be used off the CMD prompt once the certificate has been downloaded. Note the command assumes the certificate is in C:\Temp
certutil –addstore –f "root" C:\Temp\GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer
- Click Start, click Start Search, type mmc, and then press ENTER.
- On the File menu, click Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Under Available snap-ins, click Certificates, and then click Add.
- Under This snap-in will always manage certificates for, click Computer account, and then click Next.
- Click Local computer, and click Finish.
- In the console tree, double-click Certificates.
- Right-click the "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" store. Click Import to import the certificate and follow the steps in the Certificate Import Wizard for GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
Step 7 concludes the process. Validate cert installation by returning to the verification section of this document. Note, you can validate per user and all users should have the installed certificate on the server.
 Installing Certificate for your local user account with Windows Server
Installing Certificate for your local user account with Windows Server
DER encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
Should you decide to only copy the certificate to a particular user either copy the certificate over to the local system or open from web once there perform the following process for the root certificate; GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
NOTE: if you added the certificate to the local system, you do not need to add to the user accounts. This process is for systems where only selected users receive the certificate.
- Double click the root certificate and select "Install Certificate"
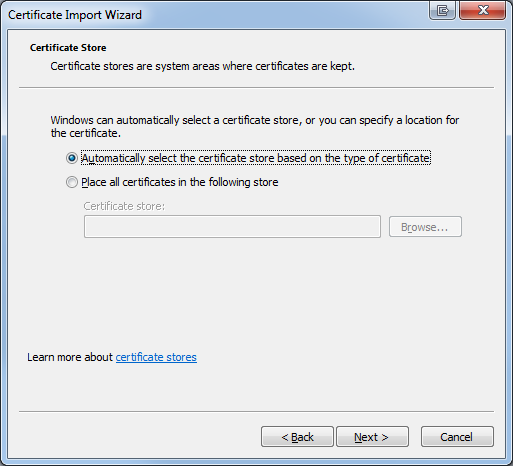
- In Wizard, click next on the first page to reach the Certificate Store page. Select "Place all certificates in the following store". Click Browse and select "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" and click OK.
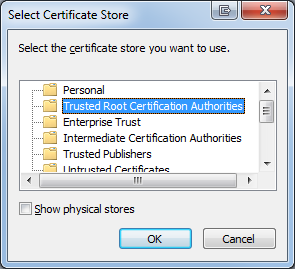
- When the wizard returns to the main page, select "Next" and then "Finish"
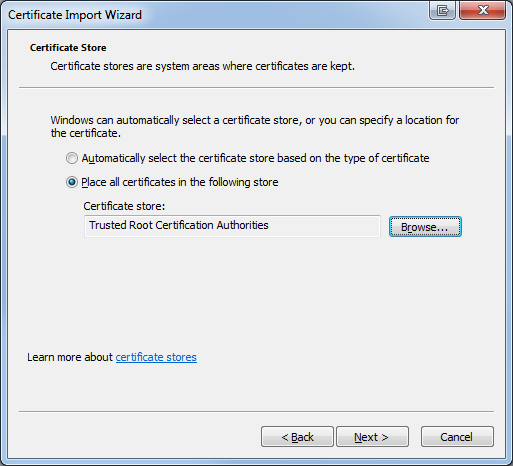
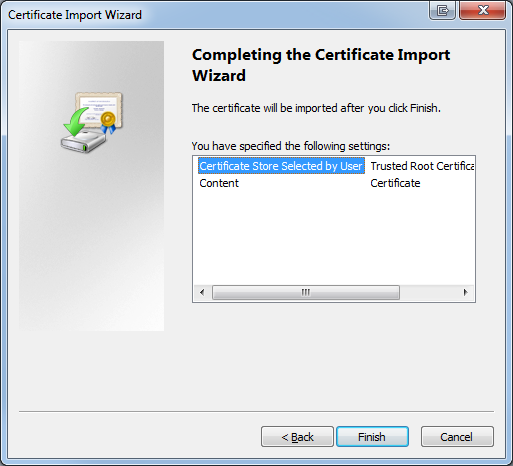
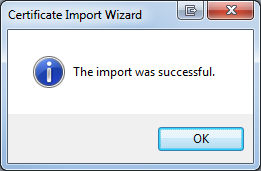
- Accept any warnings presented about root trust and click OK on the dialog box reporting the installation was successful.
![]() Deployment Note: Firefox
Deployment Note: Firefox
Firefox, if in use, installation is done within the browser itself. The certificate will be installed in the Certificate Manager for the browser and cert is imported using the same options. Install the root certificate using the following process:
- Open Firefox, on the top right hand side open menu bar and select "Options"
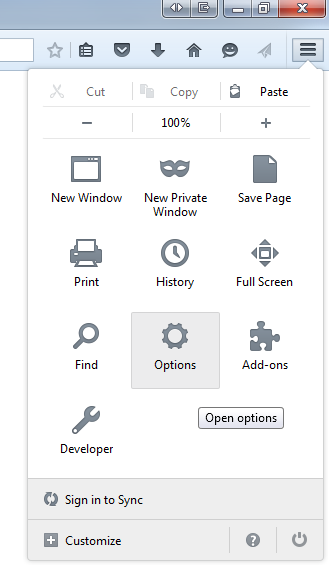
- On page, click Advanced on the left menu, select Certificates on the top and then "View Certificates".
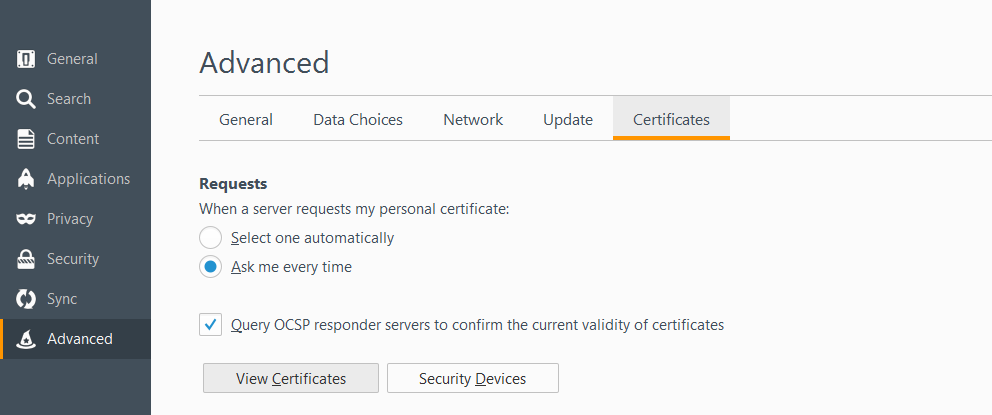
- Click on the Authorities tab and click "Import".

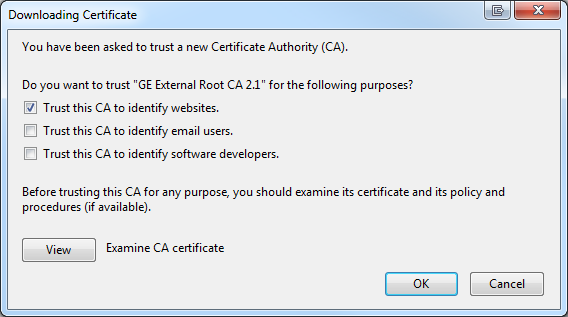
- Import the certificate and be sure to check the "Trust this CA to identify websites." And click OK.
![]() Deployment Note for older versions of Microsoft Windows Operating Systems and Microsoft Internet Explorer
Deployment Note for older versions of Microsoft Windows Operating Systems and Microsoft Internet Explorer
Please note that in some cases certificate installation validation may fail with older versions of Server and Internet Explorer, e.g. Server 2003 using Internet Explorer 7. Failures in this case is often due to a lack of support for higher level TLS standards or due to enhanced security controls. If this occurs in your installation, please try to use a different browser, e.g. Google Chrome or a modern version of Internet Explorer, to test.
![]() Deployment Note: Enhanced Internet Security Controls and Windows Server 2008 and Server 2012
Deployment Note: Enhanced Internet Security Controls and Windows Server 2008 and Server 2012
By default the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration is enabled on most Windows servers. This may cause some issues when accessing certain websites including GE’s cert validation tool. For more information on this control, please visit https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd883248(v=ws.10).aspx.
If you choose to disable IE ESC, the following process may be used:
- Open up Server Manager. It should open by default when you access your instance, but if not you can pull this up by going to your Start button -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> Server Manager
- Once in the Server Manager you will see under the Security Information an option for Configure IE ESC, noted as #1 below
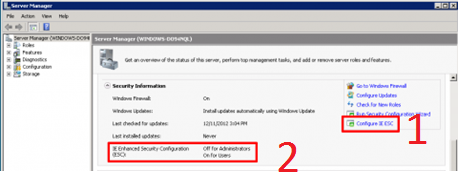
- You can choose to Enable/Disable it for just the Administrator account or for all User accounts:
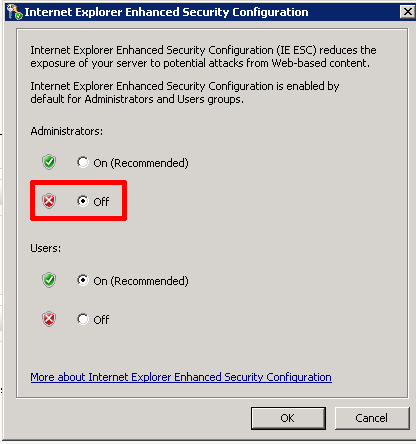
- Once the form closes, you will be returned to the Server manager where you can inspect to insure that IE ESC has been disabled for the proper user context, noted as #2 below.

Deployment Note: Visually confirming certificate installation on Microsoft Windows based Servers
The following scenarios are used to verify the installation of the certificate.
Scenario 1 – Microsoft cert store for everything except Firefox
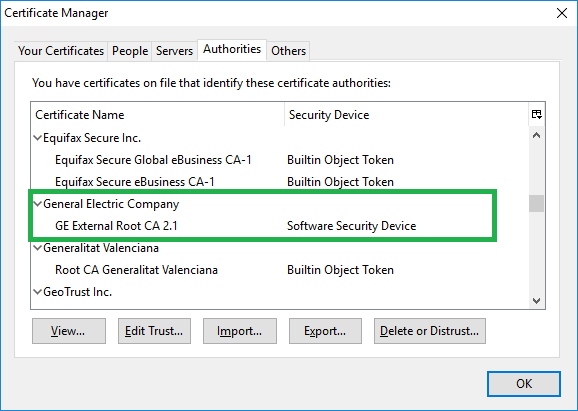
- Open from the command prompt certmgr.msc and manually browse to the Trusted root to see the certificate installed.
- Screenshot follows. Look to confirm that GE External Root CA 2.1 is present.

Scenario 2 – Cert store for Firefox
- GUI testing involves opening Firefox, going to the tools menu, then Options, Advanced, Security, View Certificates.
- Screenshot follows. Note depending on usage there may be additional GE certificates. This is ok.
 Installing Certificate on Enterprise, Amazon, and Oracle Linux release 7 and greater
Installing Certificate on Enterprise, Amazon, and Oracle Linux release 7 and greater
PEM encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt.
Procedurally, certificate will be installed to the trusted anchors. To add perform the following procedure. Note this process has been tested for both Enterprise Linux and Oracle Linux and relies on the ca-certificates package being installed on the target server.
- Copy the certificate to your home (or other common) directory using sFTP/SCP or download it via wget or cURL from the above URLs.
- Enable the dynamic CA configuration feature by typing:
sudo update-ca-trust enable
- Add new certificate as new file to /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/:
sudo cp GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/
- Update CA trust by entering :
sudo update-ca-trust extract
- Validate cert installation by typing the following command. You should not see an SSL error. You may see random characters, which is acceptable.
wget --no-cache https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -e https_proxy=PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
orcurl https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -x PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
 Installing Certificate for Linux by adding to ca-bundle.crt file
Installing Certificate for Linux by adding to ca-bundle.crt file
PEM encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt.
Procedurally, certificate will be added to the ca-bundle.crt file to include them as trusted CA anchors. To add perform the following procedure. NOTE, YOU MAY NEED TO SU TO ROOT FOR THIS PROCESS.
- Copy the certificate to your home (or other common) directory using sFTP/SCP or download it via wget or cURL from the above URLs.
- As root perform the following commands.
cat GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt >> /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
- Validate cert installation by typing the following command. You should not see an SSL error. You may see random characters, which is acceptable.
wget --no-cache https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -e https_proxy=PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
orcurl https://certcheck.pitc.apps.ge.com/imagenew.png -x PITC-Zscaler-Americas-Cincinnati3PR.proxy.corporate.ge.com:80
 Install Certificate on a WebSphere Application Server
Install Certificate on a WebSphere Application Server
DER encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer.
In Linux, copy/SCP the GE certificate files to a location on your WebSphere linux server
Add the certificate to the default WebSphere trust store:
- Login to the WebSphere Application server DMGR admin console with your administrator id.
- Expand the Security section
- Select SSL certificate and key management
- Select Key stores and certificates
- Select CellDefaultTrustStore
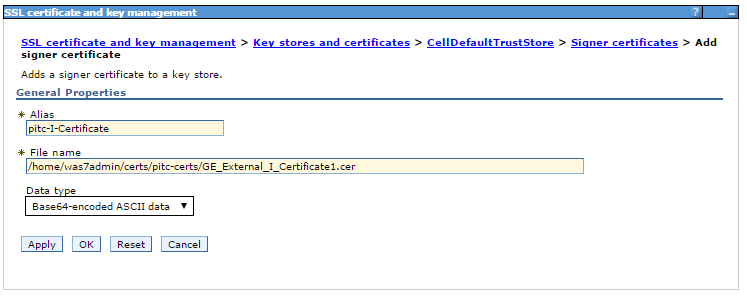
- Under Additional Properties > Select Signer Certificates
- Click the Add button
- Enter a unique Alias name such as ge_certificate
- In File name enter the directory path location to the certificate file: /home/username/certs/ge-certs/GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.cer
- click OK
- click Save
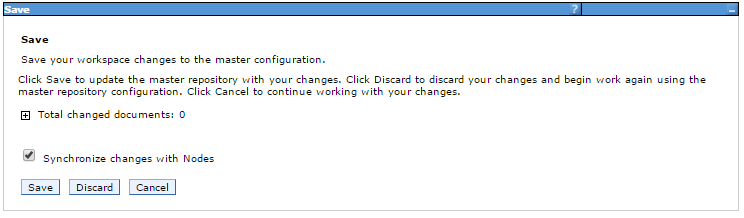
Save the changes to the master repository
- Select System Administration
- Select Save changes to master repository
- Check Synchronize changes with Nodes
- Click Save
Restart any servers as necessary.
 Installing GE Certificate in a *nix Java Store
Installing GE Certificate in a *nix Java Store
PEM encoded certificate is needed: GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt.
Each installed version of Java requires an "import" of the GE certificate as shown below.
- Download the certificate onto the target machine
- Determine where your Java is installed and where the certificate store is. In this example the cert store is at /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/lib/security/cacerts
- The GE Certificate has been placed in the /tmp directory. If yours is different please take note and update the below examples.
- Using the keytool command to import the certificate:
sudo keytool -import -alias ge.external2 -keystore /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/lib/security/cacerts -file /tmp/GE_External_Root_CA_2_1.crt
- Do this for each version of Java installed then test the Java application.
More information: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/security/toolsign/rstep2.html
If you run into issues and need additional assistance please contact your IT help desk.